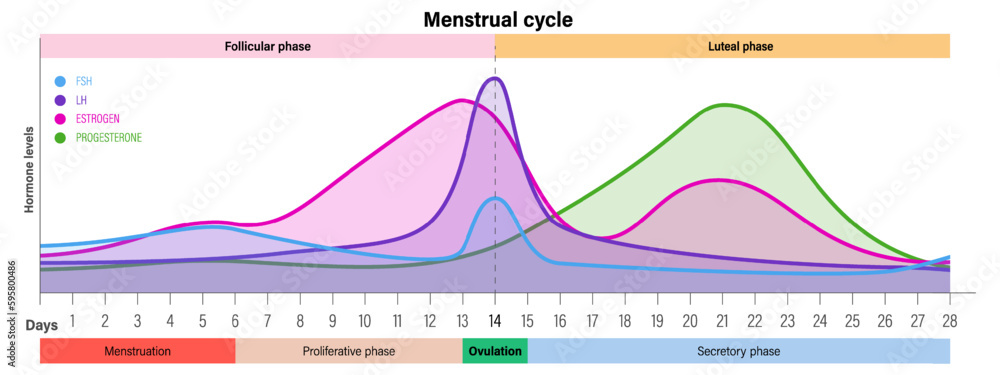
Menstrual Cycle Hormone Levels Menstrual Proliferative Ovulation And Menstruation is the cyclic, orderly sloughing of the uterine lining, in response to the interactions of hormones produced by the hypothalamus, pituitary, and ovaries. the menstrual cycle may be divided into two phases: (1) follicular or proliferative phase, and (2) the luteal or secretory phase. High estrogen levels cause a negative feedback effect on fsh, halting maturation of the follicle, while high progesterone levels causes a negative feedback effect on lh, and inhibits ovulation.
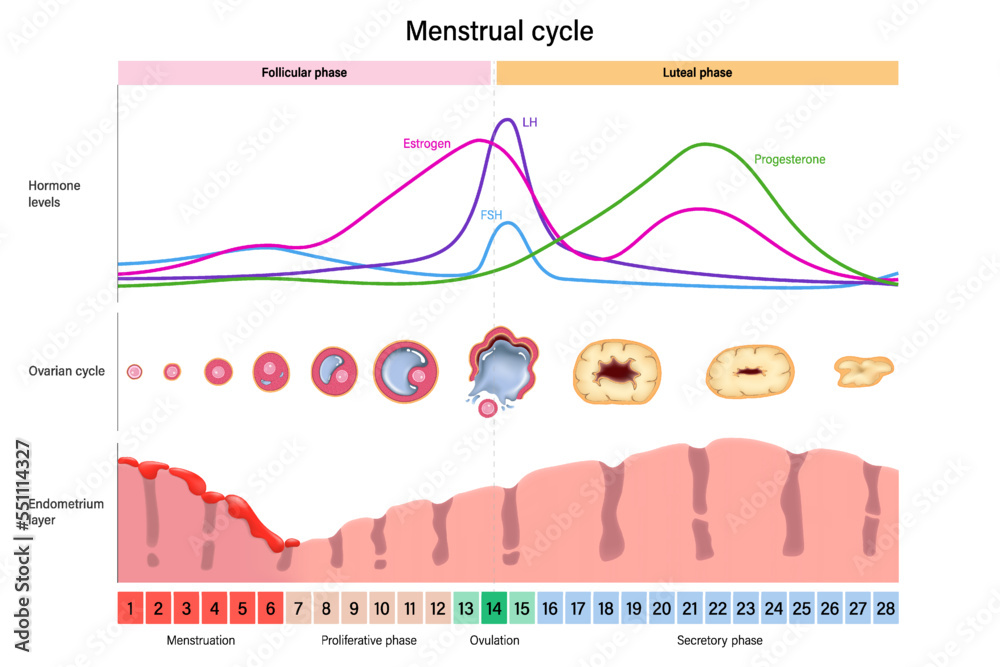
Menstrual Cycle Hormone Levels Ovarian Cycle And Endometrium Layer The menstrual cycle has two main phases. the follicular phase, or proliferative phase, normally makes up the first 10–16 days of the cycle. the luteal, or secretory, phase comes right after ovulation and lasts for about 14 days, ending with menstruation if pregnancy didn’t occur. Menstrual cycle, recurring fluctuations in hormone levels that produce physical changes in the uterus and ovaries to prepare the female body for pregnancy. in adult women, the menstrual cycle lasts anywhere from 21 to 40 days, with the average being 28 days. Ovulation typically occurs about 14 days after the start of your menstrual cycle. as the presence of progesterone, a hormone vital to support the early stages of pregnancy, and lsh increases, the level of estrogen temporarily decreases. Differentiate among the phases of the menstrual cycle. the follicular phase begins with an increase in follicle stimulation hormone ( fsh ), which causes increases in luteinizing hormone ( lh ) and gonadotropin releasing hormone ( gnrh ).

Menstrual Cycle Hormone Levels Menstrual Proliferative Stock Vector Ovulation typically occurs about 14 days after the start of your menstrual cycle. as the presence of progesterone, a hormone vital to support the early stages of pregnancy, and lsh increases, the level of estrogen temporarily decreases. Differentiate among the phases of the menstrual cycle. the follicular phase begins with an increase in follicle stimulation hormone ( fsh ), which causes increases in luteinizing hormone ( lh ) and gonadotropin releasing hormone ( gnrh ). Following ovulation, the follicle remains luteinised, secreting oestrogen and now also progesterone, reverting back to negative feedback on the hpg axis. this, together with inhibin (inhibits fsh) stalls the cycle in anticipation of fertilisation. What is the menstrual cycle? the menstrual cycle is a complex series of physiological changes that occur in women of reproductive age on a monthly basis. the end result is the production of an ovum and thickening of the endometrium to allow for implantation, should fertilisation should occur. Ovulation marks the transition from the follicular phase to the subsequent phases of the menstrual cycle. the proliferative and follicular phases are integral parts of the menstrual cycle. during the proliferative phase, the uterus prepares for potential pregnancy, while the follicular phase involves the maturation of the dominant follicle. There are four phases in the uterine cycle: menstruation, proliferative phase, ovulation, and secretory (before period bleeding) (1). a menstrual cycle starts on the first day of your period and ends the day before your next period begins.

Menstrual Cycle Hormone Levels Menstrual Proliferative Stock Vector Following ovulation, the follicle remains luteinised, secreting oestrogen and now also progesterone, reverting back to negative feedback on the hpg axis. this, together with inhibin (inhibits fsh) stalls the cycle in anticipation of fertilisation. What is the menstrual cycle? the menstrual cycle is a complex series of physiological changes that occur in women of reproductive age on a monthly basis. the end result is the production of an ovum and thickening of the endometrium to allow for implantation, should fertilisation should occur. Ovulation marks the transition from the follicular phase to the subsequent phases of the menstrual cycle. the proliferative and follicular phases are integral parts of the menstrual cycle. during the proliferative phase, the uterus prepares for potential pregnancy, while the follicular phase involves the maturation of the dominant follicle. There are four phases in the uterine cycle: menstruation, proliferative phase, ovulation, and secretory (before period bleeding) (1). a menstrual cycle starts on the first day of your period and ends the day before your next period begins.
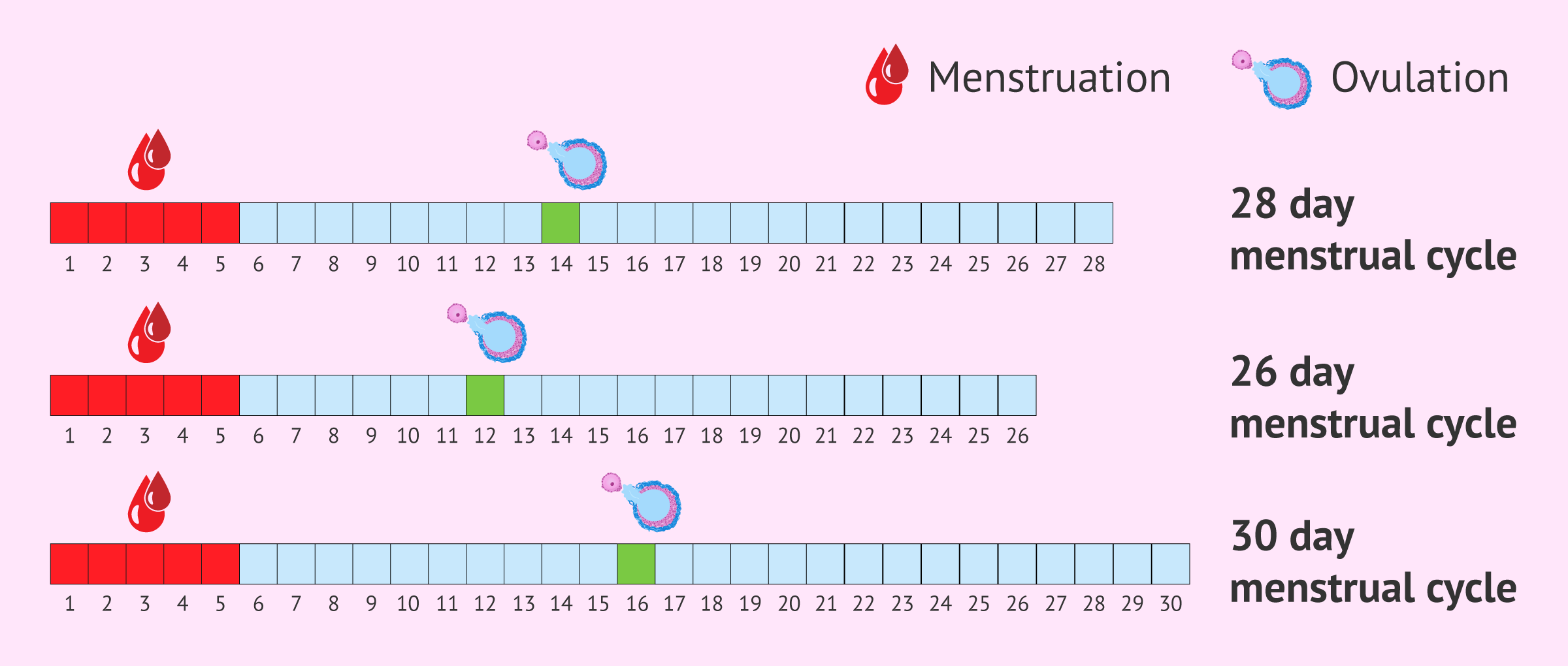
Menstrual Cycle Chart Vector Menstrual Proliferative Vrogue Co Ovulation marks the transition from the follicular phase to the subsequent phases of the menstrual cycle. the proliferative and follicular phases are integral parts of the menstrual cycle. during the proliferative phase, the uterus prepares for potential pregnancy, while the follicular phase involves the maturation of the dominant follicle. There are four phases in the uterine cycle: menstruation, proliferative phase, ovulation, and secretory (before period bleeding) (1). a menstrual cycle starts on the first day of your period and ends the day before your next period begins.

Menstrual Cycle Chart Vector Menstrual Proliferative Vrogue Co