
Solved Solution Calculations 5 Calculate The Molarity Of A Chegg How do i calculate the molarity of 7.24 * 10^2 ml of solution containing 22.4 g of potassium iodide? chemistry solutions molarity. "0.18 mol l"^( 1) right from the start, you know that the molarity of solution decreased upon the addition of water, which is what diluting a solution implies. the underlying principle behind a dilution is that you can decrease the concentration of a solution by increasing its volume while keeping the number of moles of solute constant. so, you can use the molarity and volume of the initial.

The Molarity Formula And How To Calculate Molarity Medium M = n v where m is molarity, n is number of moles and v is volume in litres. therefore: n = v.m = (20 1000) x 0.1 = 0.002 moles the equation tells you that 1 mole of citric acid reacts with 3 moles of naoh, so you must have had (0.002 3) = 0.00067 moles of citric acid in your orange juice. The molarity of the silver nitrate solution is 0.394 mm. the balanced chemical equation for this double replacement reaction looks like this agn o3(aq) kcl(aq) → agcl(s) kn o3(aq) notice that you have a 1:1 mole ratio between silver nitrate and potassium chloride, which means that you need 1 mole of silver nitrate for every 1 mole of potassium chloride in order for the reaction to take. How do we prepare a 500 ⋅ ml volume of 0.077 ⋅ mol ⋅ l−1 solution with respect to sodium chloride? what is the osmolarity of this solution? chemistry solutions molarity. Molarity is defined as moles of solutes in one litre of solution. molarity = moles of solute volume of solution (in litres) molarity = 1 mol 1 l = 1 mol l = 1 m.

Molarity And Molality Calculations Examples Pharmd Info How do we prepare a 500 ⋅ ml volume of 0.077 ⋅ mol ⋅ l−1 solution with respect to sodium chloride? what is the osmolarity of this solution? chemistry solutions molarity. Molarity is defined as moles of solutes in one litre of solution. molarity = moles of solute volume of solution (in litres) molarity = 1 mol 1 l = 1 mol l = 1 m. There is only one definition of a mole. a mole is the quantity of a substance that has the same number of particles as are found in exactly 12 g of carbon 12. this number, avogadro's number, is 6.022 × 10²³. this definition, however, leads to several different methods for determining the number of moles of a substance based on the number of particles molar mass volume and molarity of a. How to calculate molarity of f e3 ? (c r2o7)2− f e2 = c r3 f e3 [ i just need help with the 3rd subquestion, but a confirmation for the other two will be greatly appreciated. ]. Molarity = mol solute liter of solution a 3 m solution of calcium chloride contains 3 moles of the solute cacl2 in one liter of solution. to convert 3 mol cacl2 to mass in grams, multiply the given moles by the molar mass: 110.978 g mol. 3mol cacl2 × 110.978g cacl2 1mol cacl2 = 300 g cacl2 (rounded to one significant figure due to 3 mol). Convert the desired component into its respective molar quantity. then use the equations for molarity and molality. this is really a chemistry question that requires algebra to solve. as stated it is missing the critical information of molecular weight. we will also assume that the given percentage is a mass ratio but it should be stated explicitly for a correct answer. molarity = moles l.
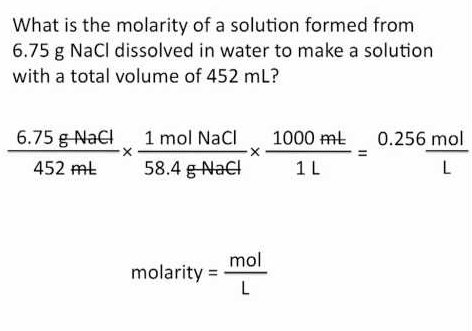
Molarity Solution Stoichiometry There is only one definition of a mole. a mole is the quantity of a substance that has the same number of particles as are found in exactly 12 g of carbon 12. this number, avogadro's number, is 6.022 × 10²³. this definition, however, leads to several different methods for determining the number of moles of a substance based on the number of particles molar mass volume and molarity of a. How to calculate molarity of f e3 ? (c r2o7)2− f e2 = c r3 f e3 [ i just need help with the 3rd subquestion, but a confirmation for the other two will be greatly appreciated. ]. Molarity = mol solute liter of solution a 3 m solution of calcium chloride contains 3 moles of the solute cacl2 in one liter of solution. to convert 3 mol cacl2 to mass in grams, multiply the given moles by the molar mass: 110.978 g mol. 3mol cacl2 × 110.978g cacl2 1mol cacl2 = 300 g cacl2 (rounded to one significant figure due to 3 mol). Convert the desired component into its respective molar quantity. then use the equations for molarity and molality. this is really a chemistry question that requires algebra to solve. as stated it is missing the critical information of molecular weight. we will also assume that the given percentage is a mass ratio but it should be stated explicitly for a correct answer. molarity = moles l.

Molarity Calculations How To Find Molarity Of A Solution Molarity = mol solute liter of solution a 3 m solution of calcium chloride contains 3 moles of the solute cacl2 in one liter of solution. to convert 3 mol cacl2 to mass in grams, multiply the given moles by the molar mass: 110.978 g mol. 3mol cacl2 × 110.978g cacl2 1mol cacl2 = 300 g cacl2 (rounded to one significant figure due to 3 mol). Convert the desired component into its respective molar quantity. then use the equations for molarity and molality. this is really a chemistry question that requires algebra to solve. as stated it is missing the critical information of molecular weight. we will also assume that the given percentage is a mass ratio but it should be stated explicitly for a correct answer. molarity = moles l.

Molarity Calculations How To Find Molarity Of A Solution