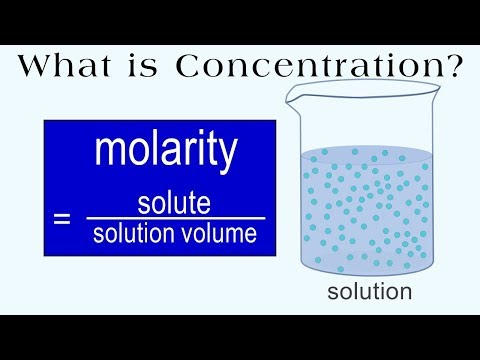
Molarity Molality Volume Mass Percent Mole Fraction Density Solution By continuing, you agree to pinterest's terms of service and acknowledge you've read our privacy policy. notice at collection. Discover recipes, home and style inspiration, and other ideas.

Molarity Molality Volume Mass Percent Mole Fraction Density Solution Descubre ideas, inspiración y contenido visual en pinterest. Ask us anything. the pinterest help center is the place to get answers to your questions, learn how to use pinterest and troubleshoot issues. Pinterest is a place of endless possibilities. you can: discover everyday inspiration shop styles you love try and learn something new create boards, save pins and make collages of all your. Pinterest’s wonderfully designed app is a constant source of inspiration, whether you’re planning a trip, remodeling your home, or finding something to wear.
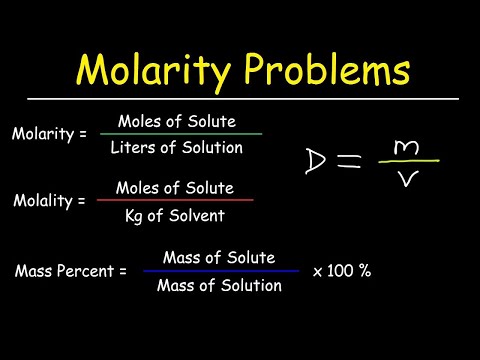
Molarity Molality Volume Mass Percent Mole Fraction Density Solution Pinterest is a place of endless possibilities. you can: discover everyday inspiration shop styles you love try and learn something new create boards, save pins and make collages of all your. Pinterest’s wonderfully designed app is a constant source of inspiration, whether you’re planning a trip, remodeling your home, or finding something to wear. Pinterest is a visual discovery engine for finding ideas like recipes, home and style inspiration, and more. set up a pinterest account to discover pins you love and save them to boards to keep your ideas organized and easy to find. It's a digital detox summer: pinterest users are looking to ditch the screens and literally touch grass this season. book retreats, nature baths and farmhouse cottage interiors will take over the summer, with searches for digital detox ideas and digital detox vision boards trending 72% and 273% respectively. the “martha stewart aesthetic” will take center stage as people embrace garden to. Pinterest es una plataforma para descubrir, guardar y compartir ideas inspiradoras sobre diversos temas.

Molarity Molality Volume Mass Percent Mole Fraction Density Solution Pinterest is a visual discovery engine for finding ideas like recipes, home and style inspiration, and more. set up a pinterest account to discover pins you love and save them to boards to keep your ideas organized and easy to find. It's a digital detox summer: pinterest users are looking to ditch the screens and literally touch grass this season. book retreats, nature baths and farmhouse cottage interiors will take over the summer, with searches for digital detox ideas and digital detox vision boards trending 72% and 273% respectively. the “martha stewart aesthetic” will take center stage as people embrace garden to. Pinterest es una plataforma para descubrir, guardar y compartir ideas inspiradoras sobre diversos temas.

Molarity Molality Volume Mass Percent Mole Fraction Densit Pinterest es una plataforma para descubrir, guardar y compartir ideas inspiradoras sobre diversos temas.