Genotype Vs Phenotype Definitions And Examples 45 Off Phenotype is a term used in genetics to refer to all the observable traits in organisms as a result of the interaction of the genotype with the environment. genotype is a term used in genetics used to refer to the genetic composition of an individual consisting of heritable genes. The genotype is the genetic code, while the phenotype is the physical expression of a trait. here is a closer look at what genotype and phenotype are, with examples.
Genotype Vs Phenotype Definitions And Examples 45 Off A key difference between phenotype and genotype is that, whilst genotype is inherited from an organism’s parents, the phenotype is not. whilst a phenotype is influenced the genotype, genotype does not equal phenotype. Genotype refers to an individual’s unique dna sequence, specifically the variants inherited from each parent for a particular gene. in contrast, phenotype is the observable expression of the genotype, shaped by the interaction between genetic makeup and environmental factors. Uncover the difference between genotype and phenotype with clear explanations, practical examples, and ratio analyses. discover how genes and environment interact to shape traits. Phenotypes can be used to determine the difference in dna sequences of people with different characteristics like height. the character of an organism is influenced by two elements which are: its expression in the genome, or its genotype as well as its interaction with environment.

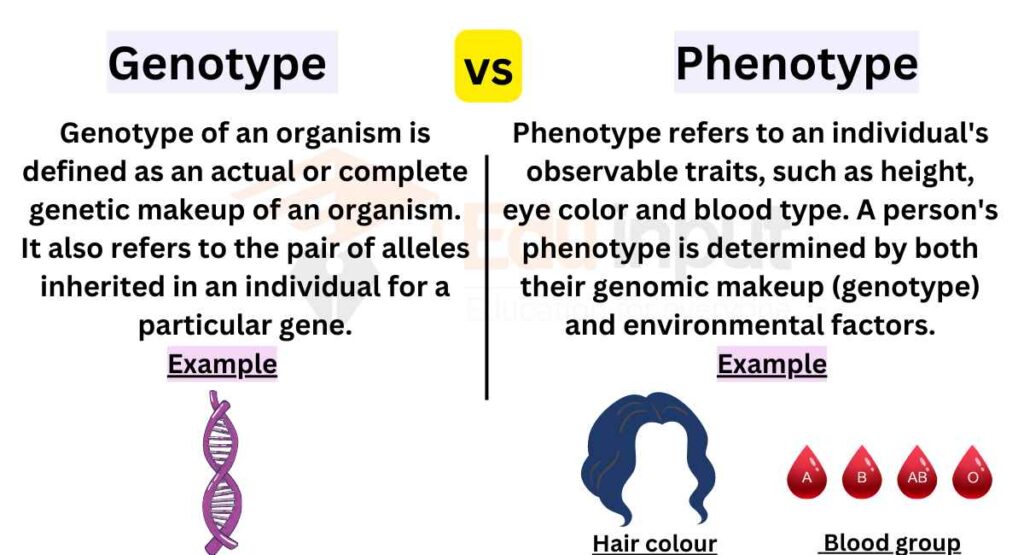
Differences Between Genotype And Phenotype Summary And 48 Off Uncover the difference between genotype and phenotype with clear explanations, practical examples, and ratio analyses. discover how genes and environment interact to shape traits. Phenotypes can be used to determine the difference in dna sequences of people with different characteristics like height. the character of an organism is influenced by two elements which are: its expression in the genome, or its genotype as well as its interaction with environment. The phenotype is the result of genetic factors, environmental influences and random genetic variations whereas genotype is the set of genes that when expressed determines the characteristic or traits of an organism. A phenotype is all of the observable characteristics of an organism, with these characteristics being influenced by the organism’s genotype and the environment the organism lives in. phenotype is how the genotype is expressed. While the genotype refers to an organism’s genetic code, the phenotype represents the physical and functional manifestation of that code. phenotypes include observable characteristics like eye color, height, body shape, or behavioral traits. these traits emerge through the interaction of genotype and environmental influences. Genotype influences potential characteristics, while phenotype showcases what you actually see, such as your eye color or height. recognizing this distinction helps clarify the complex relationship between genetics and environment.

Differences Between Genotype And Phenotype Summary And 48 Off The phenotype is the result of genetic factors, environmental influences and random genetic variations whereas genotype is the set of genes that when expressed determines the characteristic or traits of an organism. A phenotype is all of the observable characteristics of an organism, with these characteristics being influenced by the organism’s genotype and the environment the organism lives in. phenotype is how the genotype is expressed. While the genotype refers to an organism’s genetic code, the phenotype represents the physical and functional manifestation of that code. phenotypes include observable characteristics like eye color, height, body shape, or behavioral traits. these traits emerge through the interaction of genotype and environmental influences. Genotype influences potential characteristics, while phenotype showcases what you actually see, such as your eye color or height. recognizing this distinction helps clarify the complex relationship between genetics and environment.