
Java Primitive Data Types Mymusing The so called primitive function f f, which was the starting point and so came first, the root meaning of primitive (lat. primus, first), is what we might call an antiderivative or integral of p p. lagrange was very influential, and others following his lead, such as cauchy, adopted his terms primitive and derivée. Find all the primitive roots of 13 13 my attempt: since that 13 13 is a prime i need to look for g g such that g13−1 ≡ 1 (mod 13) g 13 1 ≡ 1 (mod 13) there are ϕ(12) = 4 ϕ (12) = 4 classes modulo 12 12 how can i find the classes?.

Github Sheinart Java Primitive Data Types2 Primitive recursion does allow the "next step provider" h h to see both inputs and the previous value, but we don't need to use that information. in most natural examples i think we don't in fact need that. finally, it may also help to go in the opposite direction: given a g g and h h, try to compute the first few values of the resulting f f. I'm trying to understand what primitive roots are for a given mod n mod n. wolfram's definition is as follows: a primitive root of a prime p p is an integer g g such that g (mod p) g (mod p) has multiplicative order p − 1 p 1 the main thing i'm confused about is what "multiplicative order" is. also, for the notation g (mod p) g (mod p), is it saying g g times mod p mod p or does it have. If u u and v v are relatively prime and of opposite parity, you do get a primitive triple, and you get all primitive triples in this way. Do holomorphic functions have primitive? ask question asked 3 years, 3 months ago modified 3 years, 3 months ago.

Java Data Types Primitive Nonprimitive Data Types If u u and v v are relatively prime and of opposite parity, you do get a primitive triple, and you get all primitive triples in this way. Do holomorphic functions have primitive? ask question asked 3 years, 3 months ago modified 3 years, 3 months ago. As others have mentioned, we don't know efficient methods for finding generators for (z pz)∗ (ℤ p ℤ) ∗ without knowing the factorization of p − 1 p 1. however, you can efficiently generate a random factored number n n, then test if n 1 n 1 is prime, and then compute primitive roots modulo n 1 n 1. see victor shoup a computational introduction to number theory and algebra. A primitive function of ex2 e x 2 ask question asked 11 years, 1 month ago modified 5 years, 6 months ago. 9 what is a primitive polynomial? i was looking into some random number generation algorithms and 'primitive polynomial' came up a sufficient number of times that i decided to look into it in more detail. i'm unsure of what a primitive polynomial is, and why it is useful for these random number generators. Answers to the question of the integral of 1 x 1 x are all based on an implicit assumption that the upper and lower limits of the integral are both positive real numbers. if we allow more generality, we find an interesting paradox. for instance, suppose the limits on the integral are from −a a to a a where a a is a real, positive number. the posted answer in term of ln ln would give ln(a.
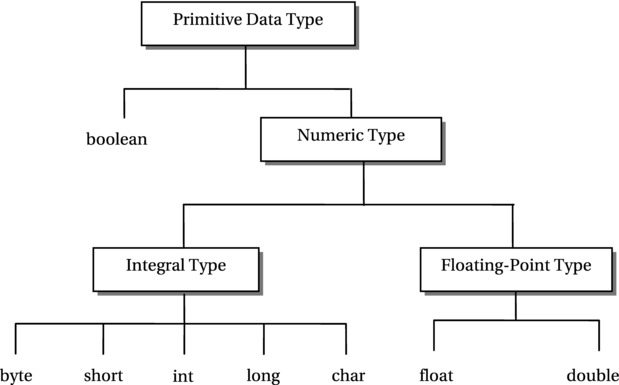
Java Primitive Datatypes And Ranges With Examples As others have mentioned, we don't know efficient methods for finding generators for (z pz)∗ (ℤ p ℤ) ∗ without knowing the factorization of p − 1 p 1. however, you can efficiently generate a random factored number n n, then test if n 1 n 1 is prime, and then compute primitive roots modulo n 1 n 1. see victor shoup a computational introduction to number theory and algebra. A primitive function of ex2 e x 2 ask question asked 11 years, 1 month ago modified 5 years, 6 months ago. 9 what is a primitive polynomial? i was looking into some random number generation algorithms and 'primitive polynomial' came up a sufficient number of times that i decided to look into it in more detail. i'm unsure of what a primitive polynomial is, and why it is useful for these random number generators. Answers to the question of the integral of 1 x 1 x are all based on an implicit assumption that the upper and lower limits of the integral are both positive real numbers. if we allow more generality, we find an interesting paradox. for instance, suppose the limits on the integral are from −a a to a a where a a is a real, positive number. the posted answer in term of ln ln would give ln(a.
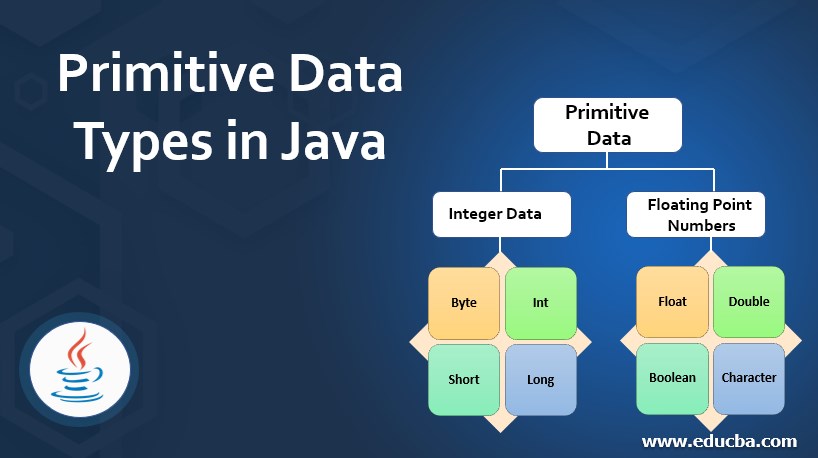
Primitive Data Types In Java Two Types With Examples To Implement 9 what is a primitive polynomial? i was looking into some random number generation algorithms and 'primitive polynomial' came up a sufficient number of times that i decided to look into it in more detail. i'm unsure of what a primitive polynomial is, and why it is useful for these random number generators. Answers to the question of the integral of 1 x 1 x are all based on an implicit assumption that the upper and lower limits of the integral are both positive real numbers. if we allow more generality, we find an interesting paradox. for instance, suppose the limits on the integral are from −a a to a a where a a is a real, positive number. the posted answer in term of ln ln would give ln(a.