
Probability Density Function Graph Normal Distribution Stock This matlab function returns the probability density function (pdf) for the one parameter distribution family specified by name and the distribution parameter a, evaluated at the values in x. Pdfnormal (x, mean, sd) returns the probability density at the value x of the normal distribution with given mean and standard deviation sd. enter the argument (s) for the function, including the symbol x. enter the minimum and maximum for the x axis and for the y axis.

Probability Density Function Graph Normal Distribution Stock The rule for a normal density function is f(x; μ , σ 2 ) = e (x μ ) 2 2 σ 2 π σ 2 the notation n(μ, σ2) means normally distributed with mean μ and variance σ2. if we say ∼ n(μ, σ2) we mean that x is distributed n(μ, σ2). about 2 3 of all cases fall within one standard deviation of the mean, that is p(μ σ ≤ x ≤ μ σ. To generate a graph of the normal distribution, we can plot many points that fall on the normal curve according to the formal definition of the probability density function (pdf) of the normal distribution, as follows:. Norm.s.inv() is a function in excel that returns the inverse of the standard normal cumulative distribution for a specified probability, and i’ll draw a graph where the x axis represents norm.s.inv() (i column) and the y axis represents grai weight (b column). Standard normal density function – all of the gaussian pdf cases, for any mean value and for any standard deviation, can be collapsed into one normalized curve called the standard normal density function.
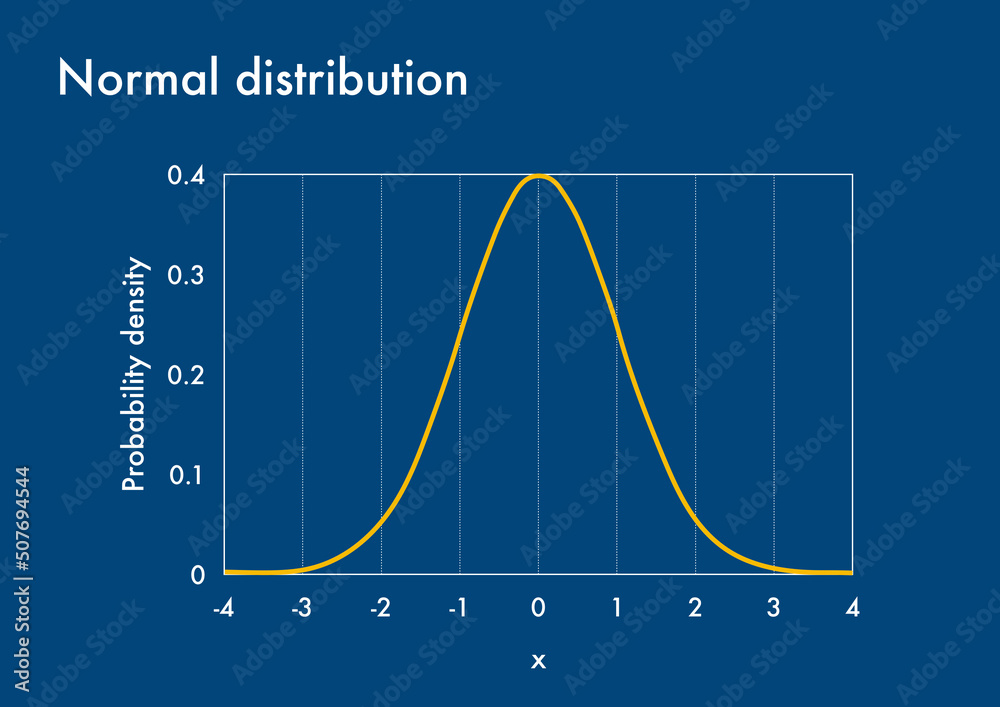
Probability Density Function Graph Of Normal Distribution Stock Norm.s.inv() is a function in excel that returns the inverse of the standard normal cumulative distribution for a specified probability, and i’ll draw a graph where the x axis represents norm.s.inv() (i column) and the y axis represents grai weight (b column). Standard normal density function – all of the gaussian pdf cases, for any mean value and for any standard deviation, can be collapsed into one normalized curve called the standard normal density function. We base our approach on a state of the art methodology that solves jssp by means of drl and graph neural network embeddings. The normal probability distribution graph, also known as the bell curve, is a method to find the value distribution of a dataset. this function depends entirely on the mean and standard deviation values received from the dataset. This function returns the cumulative probability from zero up to some input value of the random variable x. technically, it returns the percentage of area under a continuous distribution curve from negative infinity to the x. Plot(pd) plots a probability density function (pdf) of the probability distribution object pd. if pd is created by fitting a probability distribution to the data, the pdf is superimposed over a histogram of the data. plot(ax,pd) plots into the axes specified by the axes graphics object ax.

Normal Distribution Curve Pdf Normal Distribution Probability We base our approach on a state of the art methodology that solves jssp by means of drl and graph neural network embeddings. The normal probability distribution graph, also known as the bell curve, is a method to find the value distribution of a dataset. this function depends entirely on the mean and standard deviation values received from the dataset. This function returns the cumulative probability from zero up to some input value of the random variable x. technically, it returns the percentage of area under a continuous distribution curve from negative infinity to the x. Plot(pd) plots a probability density function (pdf) of the probability distribution object pd. if pd is created by fitting a probability distribution to the data, the pdf is superimposed over a histogram of the data. plot(ax,pd) plots into the axes specified by the axes graphics object ax.
Probability Density Function Graph Of Normal Distribution Download This function returns the cumulative probability from zero up to some input value of the random variable x. technically, it returns the percentage of area under a continuous distribution curve from negative infinity to the x. Plot(pd) plots a probability density function (pdf) of the probability distribution object pd. if pd is created by fitting a probability distribution to the data, the pdf is superimposed over a histogram of the data. plot(ax,pd) plots into the axes specified by the axes graphics object ax.

Probability Density Function Graph Of Normal Distribution Download