
Coursework 2 Of 2 Unconstrained Optimization Pdf Report both the maximum function value and the value (s) of x at which the function value is attained. maxx75 (3x 5)2− (6x−2)2 5) solve the following (unconstrained) optimization problem in one variable (x) where a and b are arbitrary constants. there are 3 steps to solve this one. In this chapter we study mathematical programming techniques that are commonly used to extremize nonlinear functions of single and multiple (n) design variables subject to no constraints.

Solved 4 Solve The Following Unconstrained Optimization Chegg The starting search range. solution: p iteration 1: xl = 0, xu = 4, d = 5¡1 (xu ¡ xl) = 2:472, x1 = xl 2 d = 2:472, x2 = xu ¡ d = 1:528. f (x1) = 0:63, f (x2) = 1:765. since f (x2) > f (x1), x¤ = x2 = 1:528, xl = xl = 0 and xu = x1 = 2:472. p. Unconstrained optimization an unconstrained optimization problem takes the form min f(x) x∈rn (4.1) for a target functional (also called objective function) f : rn → r. in this chapter and throughout most of our discussion on optimization, we will assume that. The types of problems that we solved in the previous section were examples of unconstrained optimization problems. that is, we tried to find local (and perhaps even global) maximum and minimum points of real valued functions f(x, y) f (x, y), where the points (x, y) (x, y) could be any points in the domain of f f. Special symbols math calculus calculus questions and answers 4) solve the following unconstrained optimization problem min ( (z 3y)' 22y (2x 2y)2 10z 4y (2t 2y) 10a 4y.

Solved 4 Solve The Following Constrained And Unconstrained Chegg The types of problems that we solved in the previous section were examples of unconstrained optimization problems. that is, we tried to find local (and perhaps even global) maximum and minimum points of real valued functions f(x, y) f (x, y), where the points (x, y) (x, y) could be any points in the domain of f f. Special symbols math calculus calculus questions and answers 4) solve the following unconstrained optimization problem min ( (z 3y)' 22y (2x 2y)2 10z 4y (2t 2y) 10a 4y. Returning to the optimization problem (p), knowing that the function f(x) is convex allows us to establish a global optimality condition that is both necessary and sufficient: theorem 10 suppose f(x) : x is convex and differentiable on x. → then x ̄ x is a global minimum if and only if f( ̄ x) = 0. Unconstrained optimization crops up in many fields under different names, and understanding how to solve these types of problems is incredibly powerful. some examples include regressing a linear function onto the data set. here we are minimizing the sum of squared error. One way to solve for max z(x), where x is a vector, is to find the first derivatives, set them equal to zero, and solve the resulting system of nonlinear equations. The following theorem describes properties that must be satisfied by a point x in order for f (x ) to be a local minimum. these properties do not guarantee that x is a local minimum, but if these properties are not satisfied, then the point is not a minimum.
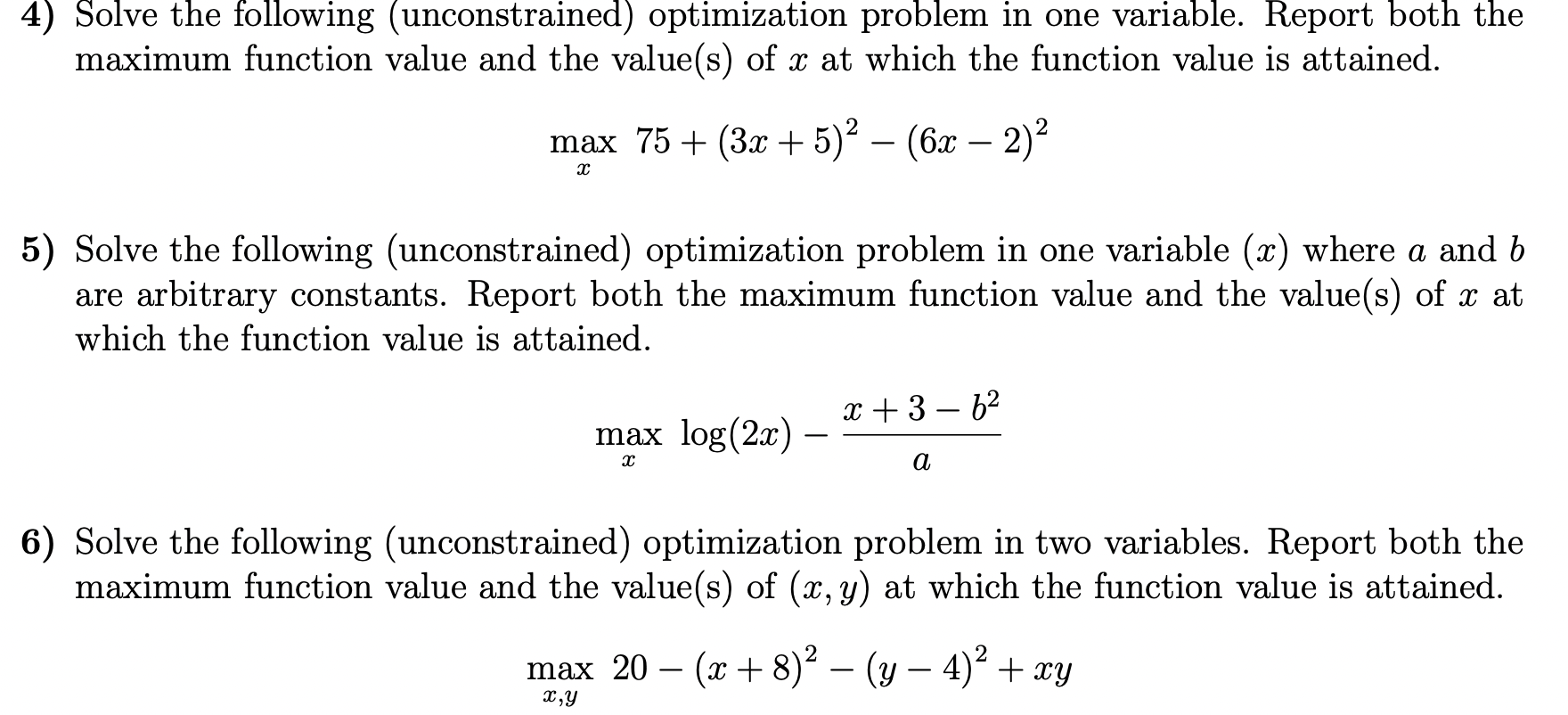
Solved 4 Solve The Following Unconstrained Optimization Chegg Returning to the optimization problem (p), knowing that the function f(x) is convex allows us to establish a global optimality condition that is both necessary and sufficient: theorem 10 suppose f(x) : x is convex and differentiable on x. → then x ̄ x is a global minimum if and only if f( ̄ x) = 0. Unconstrained optimization crops up in many fields under different names, and understanding how to solve these types of problems is incredibly powerful. some examples include regressing a linear function onto the data set. here we are minimizing the sum of squared error. One way to solve for max z(x), where x is a vector, is to find the first derivatives, set them equal to zero, and solve the resulting system of nonlinear equations. The following theorem describes properties that must be satisfied by a point x in order for f (x ) to be a local minimum. these properties do not guarantee that x is a local minimum, but if these properties are not satisfied, then the point is not a minimum.

Solved 4 Solve The Following Unconstrained Optimization Chegg One way to solve for max z(x), where x is a vector, is to find the first derivatives, set them equal to zero, and solve the resulting system of nonlinear equations. The following theorem describes properties that must be satisfied by a point x in order for f (x ) to be a local minimum. these properties do not guarantee that x is a local minimum, but if these properties are not satisfied, then the point is not a minimum.