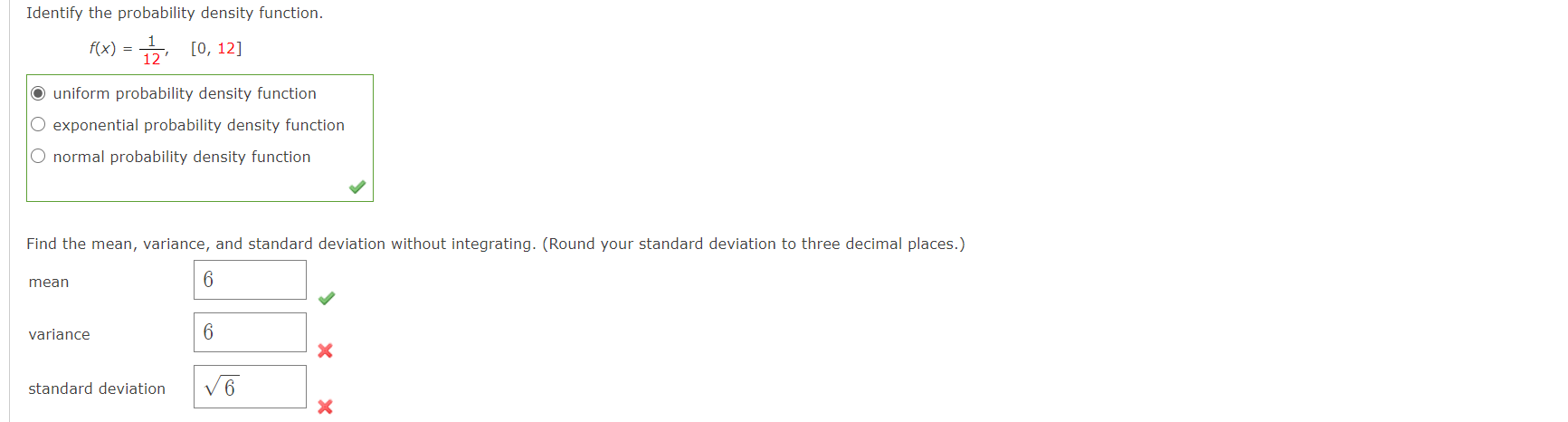
Solved Identify The Probability Density Function F X 1 Chegg Question: figure 1: probability density function 1 2 1. consider a continuous random variable represented by the probability density function (pdf) in figure 1. (a) what is the value of the constant c that makes the function a valid pdf?. Determine p( x > 4) . two such batteries are needed by a piece of electronic equipment. this equipment will only operate if both batteries are still functional. if two new batteries are fitted to this equipment, determine the probability that this equipment will stop working within the next 40 hours. 59 fs1 d , p( x > 4) = , 75.
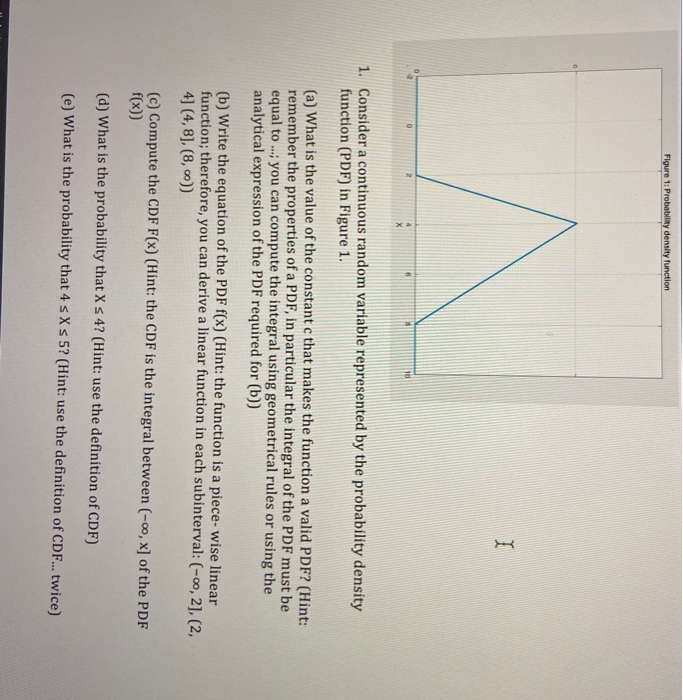
Solved Figure 1 Probability Density Function 1 2 1 Chegg The probability density function (" p.d.f. ") of a continuous random variable x with support s is an integrable function f (x) satisfying the following: f (x) is positive everywhere in the support s, that is, f (x)> 0, for all x in s. This tutorial provides a basic introduction into probability density functions. it explains how to find the probability that a continuous random variable such as x in somewhere between two values by evaluating the definite integral from a to b. The function fx(x) f x (x) gives us the probability density at point x x. it is the limit of the probability of the interval (x, x Δ] (x, x Δ] divided by the length of the interval as the length of the interval goes to 0 0. Here’s the best way to solve it. identify the areas corresponding to the intervals 1 ≤ x <3, 3 ≤ x <4, and 4 ≤ x <5 on the probability density function (pdf). not the question you’re looking for? post any question and get expert help quickly.
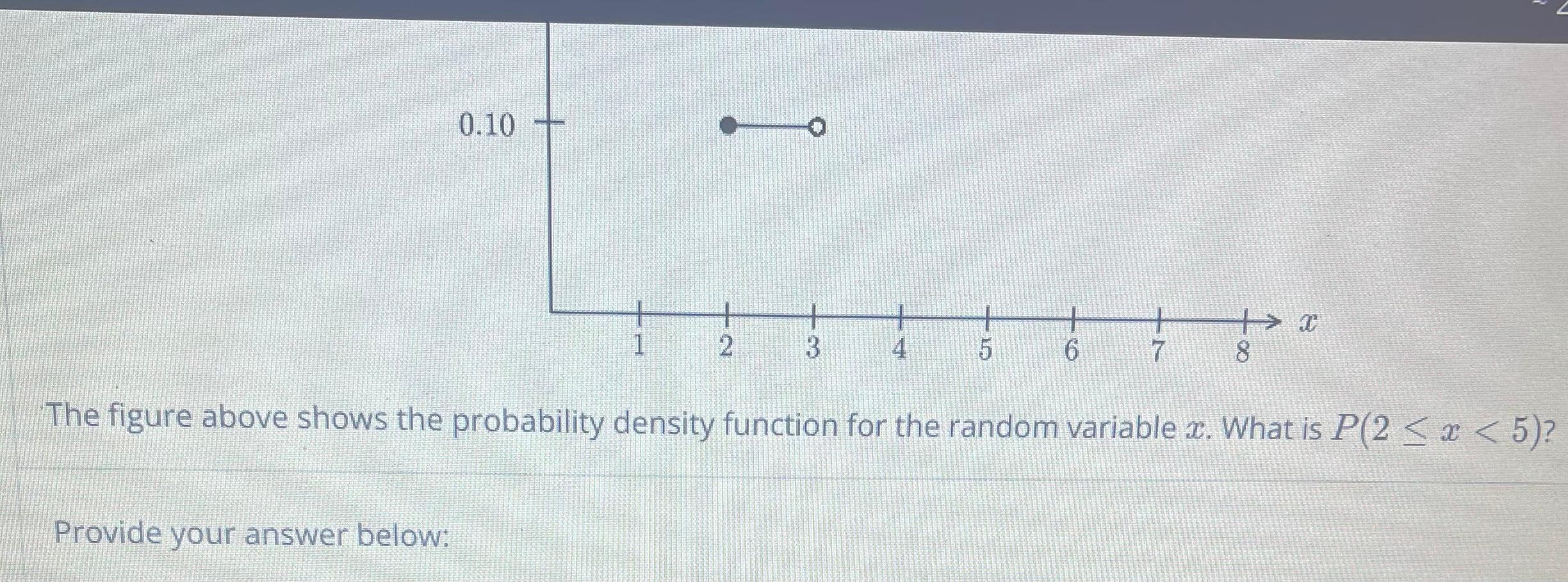
Solved The Figure Above Shows The Probability Density Chegg The function fx(x) f x (x) gives us the probability density at point x x. it is the limit of the probability of the interval (x, x Δ] (x, x Δ] divided by the length of the interval as the length of the interval goes to 0 0. Here’s the best way to solve it. identify the areas corresponding to the intervals 1 ≤ x <3, 3 ≤ x <4, and 4 ≤ x <5 on the probability density function (pdf). not the question you’re looking for? post any question and get expert help quickly. Just as for discrete random variables, we can talk about probabilities for continuous random variables using density functions. the probability density function (pdf), denoted f f, of a continuous random variable x x satisfies the following:. The probability density function of the exponential distribution is de ned as f(x) = e x for x 0 and f(x) = 0 for x < 0. it is used to used measure lengths of arrival times like the time until you get the next email. There are 2 steps to solve this one. it is given that figures 1 & 2 represent the graph of probability density functions for two continuo not the question you’re looking for? post any question and get expert help quickly. There are 3 steps to solve this one. figure 1: probability density function (25 points) consider a continuous random variable represented by the probability density function (pdf) in figure 1. (a) what is the value of the constant c that makes the function a valid pdf?.