Stages Of Cellular Respiration Diagram
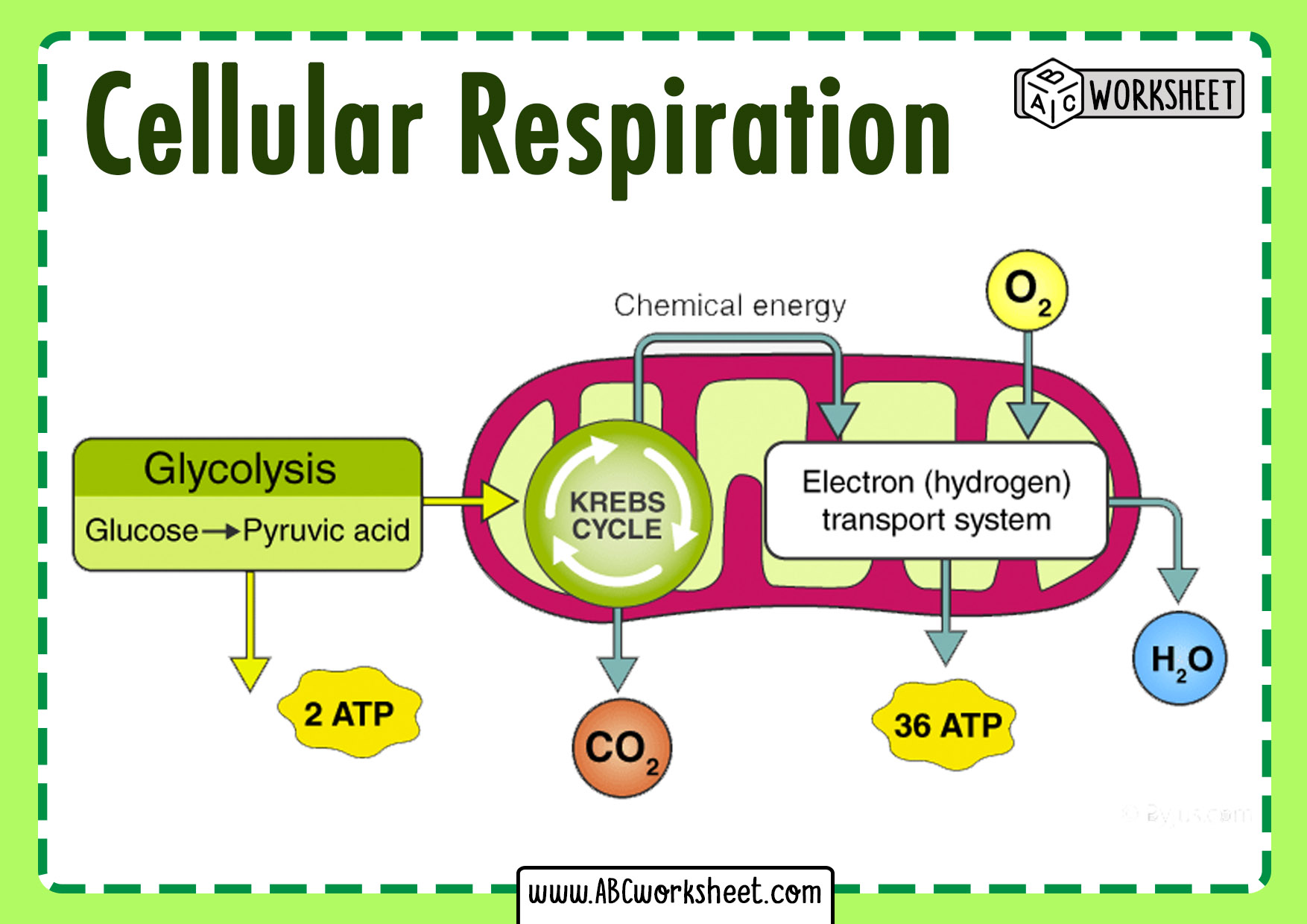
Simple Cellular Respiration Diagram Cellular respiration involves many chemical reactions. the reactions can be summed up in this equation: c 6 h 12 o 6 6o 2 → 6co 2 6h 2 o chemical energy (in atp) the reactions of cellular respiration can be grouped into three stages: glycolysis (stage 1), the krebs cycle, also called the citric acid cycle (stage 2), and electron. The space enclosed by the inner membrane is called the matrix. the second stage of cellular respiration, the krebs cycle, takes place in the matrix. the third stage, electron transport, takes place on the inner membrane. figure 5.9.6 5.9. 6: the structure of a mitochondrion is defined by an inner and outer membrane.
:max_bytes(150000):strip_icc()/cellular_respiration-8fcc3f1ad3e54a828dabc02146ce4307.jpg)
Cellular Respiration Definition And Examples Biology Online Dictionary The equation for aerobic respiration shows glucose being combined with oxygen and adp to produce carbon dioxide, water, and atp: c6h12o6 (glucose) 6o2 36 adp (depleted atp) 36 pi (phosphate groups)→ 6co2 6h2o 36 atp. you can see that once it is completely broken down, the carbon molecules of glucose are exhaled as six molecules of. Here is the definition of aerobic respiration, its significance, the organisms that rely on it, and the stages involved. aerobic respiration definition. aerobic respiration is a cellular process in the cell uses oxygen to metabolize glucose and produce energy in the form of adenosine triphosphate . it is the most efficient form of cellular. Cellular respiration is a complex biochemical pathway that comprises four stages which are briefly discussed below: 1) glycolysis. in the first step of cellular respiration, glycolysis, a glucose molecule undergoes a series of chemical transformations in the cytosol of all living cells. it is the only step that is shared by all types of. 4.5: cellular respiration. cellular respiration is the process of oxidizing food molecules, like glucose, to carbon dioxide and water. \ [c 6h {12}o {6} 6o 2 6h 2o → 12h 2o 6 co 2 \] the energy released is trapped in the form of atp for use by all the energy consuming activities of the cell. the process occurs in two phases:.

Comments are closed.