
Image Classification Unsupervised Pdf Statistical Classification In this post we will see how to download a landsat satellite image and image classification in qgis. there are many software tools available for image classification such as arcgis, erdas imagin, but these are not open source software. Lab 6 image classification supervised vs. unsupervised approaches supervised image analyst "supervises" the selection of spectral classes that represent patterns or land cover features that the analyst can recognize prior decision.
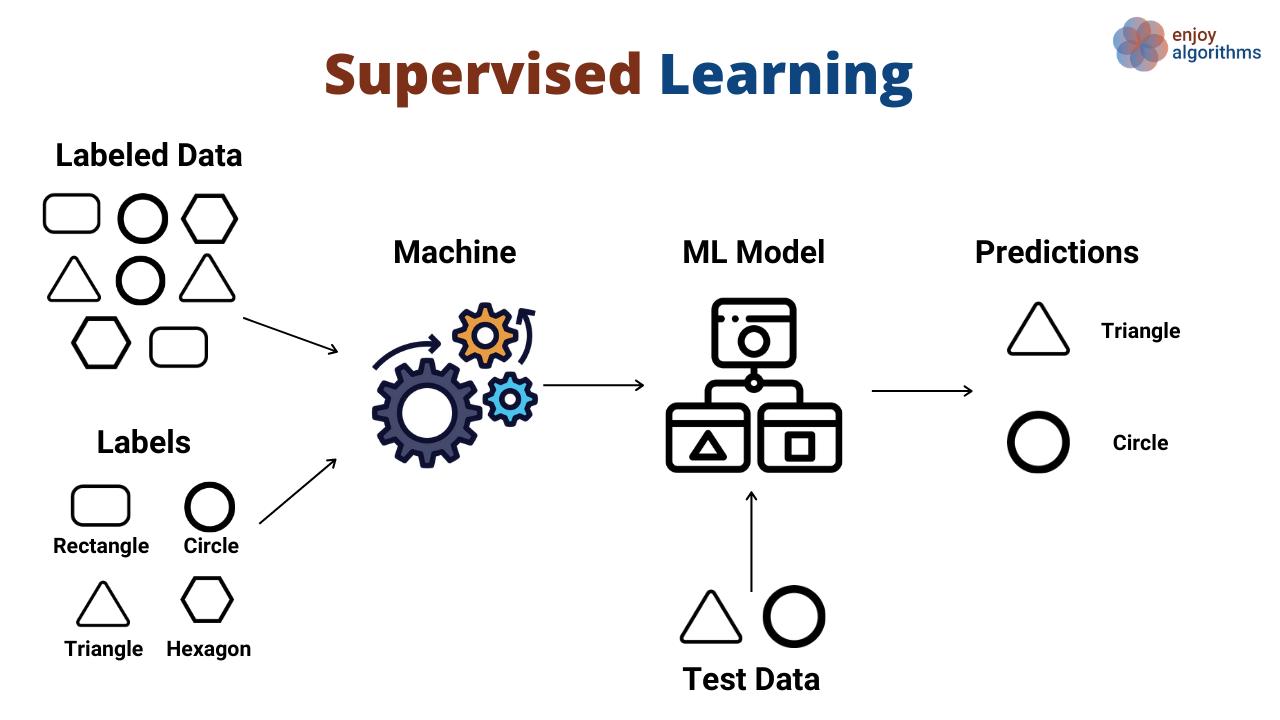
Supervised And Unsupervised Classification In Remote Sensing Gis What are the main differences between supervised and unsupervised classification? you can follow along as we classify in arcgis. in supervised classification, you select training samples and classify your image based on your chosen samples. Supervised classification principles the classifier learns the characteristics of different thematic classes – forest, marshy vegetation, agricultural land, turbid water, clear water, open soils, manmade objects, desert etc. Ser or not, i.e. supervised or unsupervised approach. pixel based image classification techniques are the most known and common approach; however, the object based classification . ay be beneficial in the case of high resolution data. pixel based approach assigns each pixel to a class; object based ap. Using different characteristics of multi domain data to efficiently capture useful features for the sonar image classification, mdctl offers a new way for transfer learning.
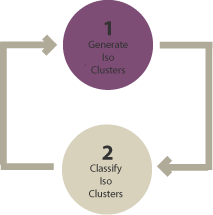
Supervised And Unsupervised Classification Ser or not, i.e. supervised or unsupervised approach. pixel based image classification techniques are the most known and common approach; however, the object based classification . ay be beneficial in the case of high resolution data. pixel based approach assigns each pixel to a class; object based ap. Using different characteristics of multi domain data to efficiently capture useful features for the sonar image classification, mdctl offers a new way for transfer learning. All the channels including ch3 and ch3t are used in this project. the image is classified to six classes including water, vegetation, thin partial clouds over ground, thin clouds, low middle thick clouds and high thick clouds plus unknown class for supervised classification. The paper focuses on what image classification, need of it, major steps for classification, different image classification techniques, comparison of supervised & unsupervised image classification. Unsupervised classifications • this is a computerized method without direction from the analyst in which pixels with similar digital numbers are grouped together into spectral classes using statistical procedures such as nearest neighbour and cluster analysis. Can we automatically group images into semantically meaningful clusters when ground truth annotations are absent? the task of unsupervised image classification remains an important, and open challenge in computer vision.

Supervised And Unsupervised Classification All the channels including ch3 and ch3t are used in this project. the image is classified to six classes including water, vegetation, thin partial clouds over ground, thin clouds, low middle thick clouds and high thick clouds plus unknown class for supervised classification. The paper focuses on what image classification, need of it, major steps for classification, different image classification techniques, comparison of supervised & unsupervised image classification. Unsupervised classifications • this is a computerized method without direction from the analyst in which pixels with similar digital numbers are grouped together into spectral classes using statistical procedures such as nearest neighbour and cluster analysis. Can we automatically group images into semantically meaningful clusters when ground truth annotations are absent? the task of unsupervised image classification remains an important, and open challenge in computer vision.

Supervised And Unsupervised Classification Unsupervised classifications • this is a computerized method without direction from the analyst in which pixels with similar digital numbers are grouped together into spectral classes using statistical procedures such as nearest neighbour and cluster analysis. Can we automatically group images into semantically meaningful clusters when ground truth annotations are absent? the task of unsupervised image classification remains an important, and open challenge in computer vision.