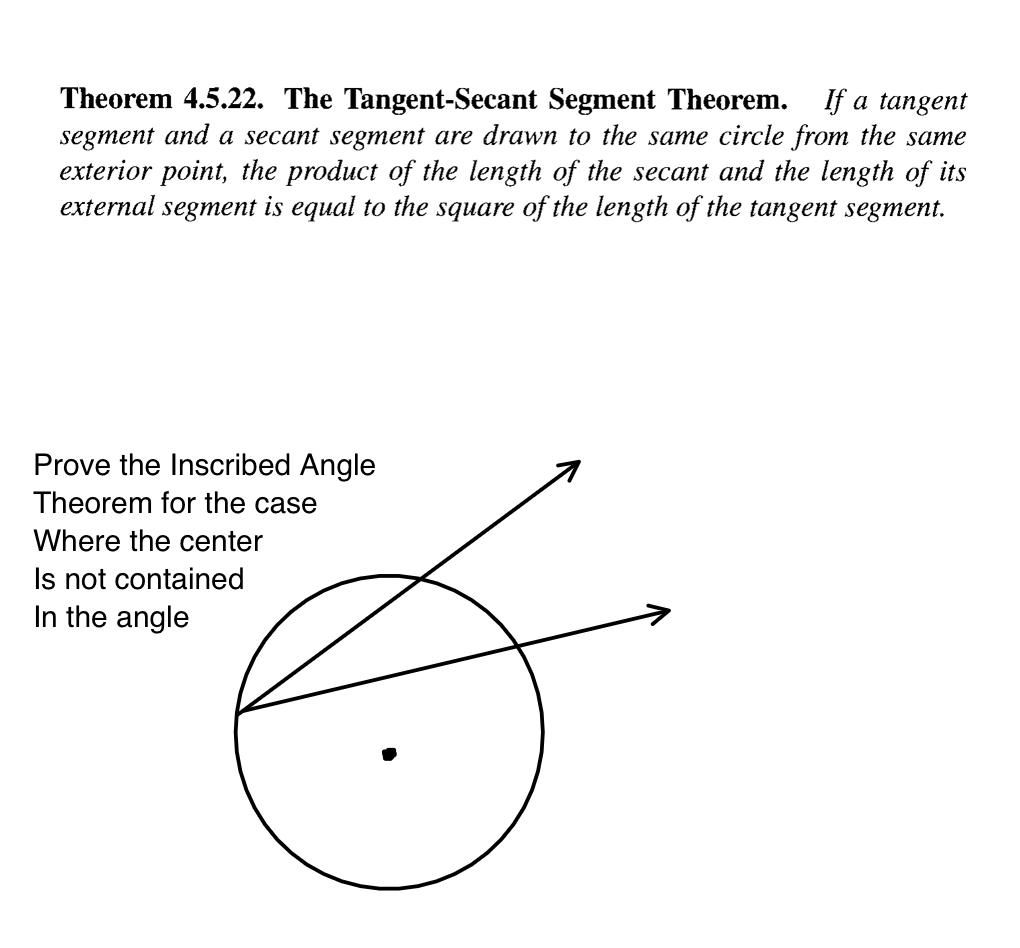
Solved Theorem 4 5 22 The Tangent Secant Segment Theorem Chegg Sine, cosine and tangent are the main functions used in trigonometry and are based on a right angled triangle. before getting stuck into the functions, it helps to give a name to each side of a right triangle: opposite is always opposite the angle. and adjacent is always next to the angle. The sum and difference formulas allow expanding the sine, the cosine, and the tangent of a sum or a difference of two angles in terms of sines and cosines and tangents of the angles themselves.

Solved Theorem 17 1 8 Tangent Secant Segment Theorem If A Chegg The meaning of tangent is an abrupt change of course : digression. how to use tangent in a sentence. The graph of tangent is periodic, meaning that it repeats itself indefinitely. unlike sine and cosine however, tangent has asymptotes separating each of its periods. The tangent is one of the six fundamental trigonometric functions in mathematics. in a right triangle, it is the ratio of the length of the side opposite a given angle to the length of the side adjacent to that angle. In trigonometry, the tangent of an angle is the ratio of the length of the opposite side to the length of the adjacent side. in other words, it is the ratio of sine and cosine function of an acute angle such that the value of cosine function should not equal to zero.
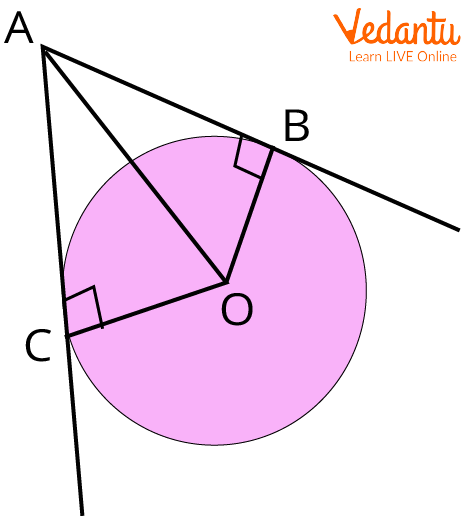
Tangent Segment Theorem Learn And Solve Questions The tangent is one of the six fundamental trigonometric functions in mathematics. in a right triangle, it is the ratio of the length of the side opposite a given angle to the length of the side adjacent to that angle. In trigonometry, the tangent of an angle is the ratio of the length of the opposite side to the length of the adjacent side. in other words, it is the ratio of sine and cosine function of an acute angle such that the value of cosine function should not equal to zero. The tangent function is one of the main six trigonometric functions and is generally written as tan x. it is the ratio of the opposite side and the adjacent side of the angle in consideration in a right angled triangle. The tangent function, along with sine and cosine, is one of the three most common trigonometric functions. in any right triangle, the tangent of an angle is the length of the opposite side (o) divided by the length of the adjacent side (a). in a formula, it is written simply as 'tan'. Its domain of definition is the entire number axis with the exception of the points $\pi 2=n\pi$, $n=\pm1,\pm2,\dots$. the tangent is an unbounded, odd and periodic (with $\pi$ as the smallest positive period) function. the tangent and the cotangent are connected by the relation. $$\tan x=\frac {1} {\operatorname {cotan}x}$$. In geometry, the tangent line (or simply tangent) to a plane curve at a given point is, intuitively, the straight line that "just touches" the curve at that point.
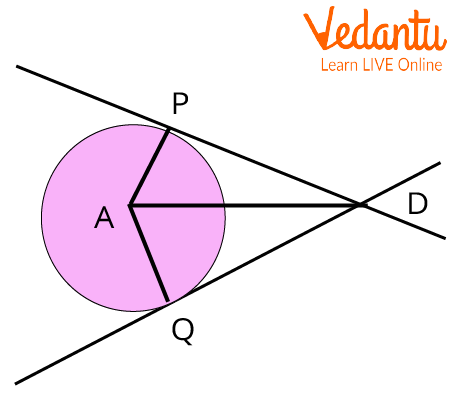
Tangent Segment Theorem Learn And Solve Questions The tangent function is one of the main six trigonometric functions and is generally written as tan x. it is the ratio of the opposite side and the adjacent side of the angle in consideration in a right angled triangle. The tangent function, along with sine and cosine, is one of the three most common trigonometric functions. in any right triangle, the tangent of an angle is the length of the opposite side (o) divided by the length of the adjacent side (a). in a formula, it is written simply as 'tan'. Its domain of definition is the entire number axis with the exception of the points $\pi 2=n\pi$, $n=\pm1,\pm2,\dots$. the tangent is an unbounded, odd and periodic (with $\pi$ as the smallest positive period) function. the tangent and the cotangent are connected by the relation. $$\tan x=\frac {1} {\operatorname {cotan}x}$$. In geometry, the tangent line (or simply tangent) to a plane curve at a given point is, intuitively, the straight line that "just touches" the curve at that point.