
Theorem 10 2 Class 10 Tangents From External Point Of Circle Are In geometry, the tangent line (or simply tangent) to a plane curve at a given point is, intuitively, the straight line that "just touches" the curve at that point. : the trigonometric function that for an acute angle is the ratio between the leg opposite to the angle when it is considered part of a right triangle and the leg adjacent.

Class 10 Theorem 10 2 The Lengths Of Tangent Drawn From An External Sine, cosine and tangent are the main functions used in trigonometry and are based on a right angled triangle. before getting stuck into the functions, it helps to give a name to each side of a right triangle: opposite is always opposite the angle. and adjacent is always next to the angle. In geometry, a tangent is the line drawn from an external point and passes through a point on the curve. one real life example of a tangent is when you ride a bicycle, every point on the circumference of the wheel makes a tangent with the road. let us understand the concept of a tangent with an example. In trigonometry, the tangent function (tan) of an angle in a right triangle is the ratio of the opposite side to the adjacent side. how is tangent related to sine and cosine? what is the pythagorean identity involving tangent? what is the derivative of the tangent function with respect to x?. There are many methods that can be used to determine the value for tangent such as referencing a table of tangents, using a calculator, and approximating using the taylor series of tangent.
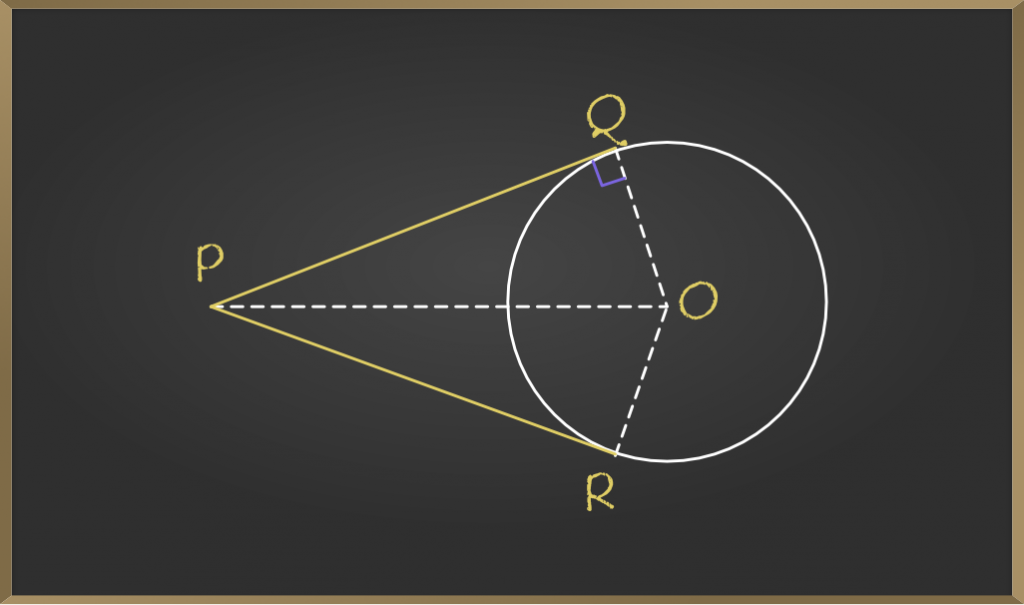
Theorem The Lengths Of Tangents Drawn From An External Point To A In trigonometry, the tangent function (tan) of an angle in a right triangle is the ratio of the opposite side to the adjacent side. how is tangent related to sine and cosine? what is the pythagorean identity involving tangent? what is the derivative of the tangent function with respect to x?. There are many methods that can be used to determine the value for tangent such as referencing a table of tangents, using a calculator, and approximating using the taylor series of tangent. Tangents, secants, arcs and their angles. the theorems and formula for the rules for theses intersections. In trigonometry, the tangent function is used to find the slope of a line between the origin and a point representing the intersection between the hypotenuse and the altitude of a right triangle. however, in both trigonometry and geometry, tangent represents the slope of some object. In this article, we explored tangent in geometry. we learned that a tangent is a line that touches a circle at one point, known as the point of tangency. we also learned that a right angle forms between the tangent line and the radius of the circle, and that tangent can be used to measure circles. The simplest definition of the tangent uses the ratios of the sides of a right triangle, and modern methods express this function as the sum of an infinite series. tangents can be calculated directly when the lengths of the sides of the right triangle are known and can also be derived from other trigonometric functions.
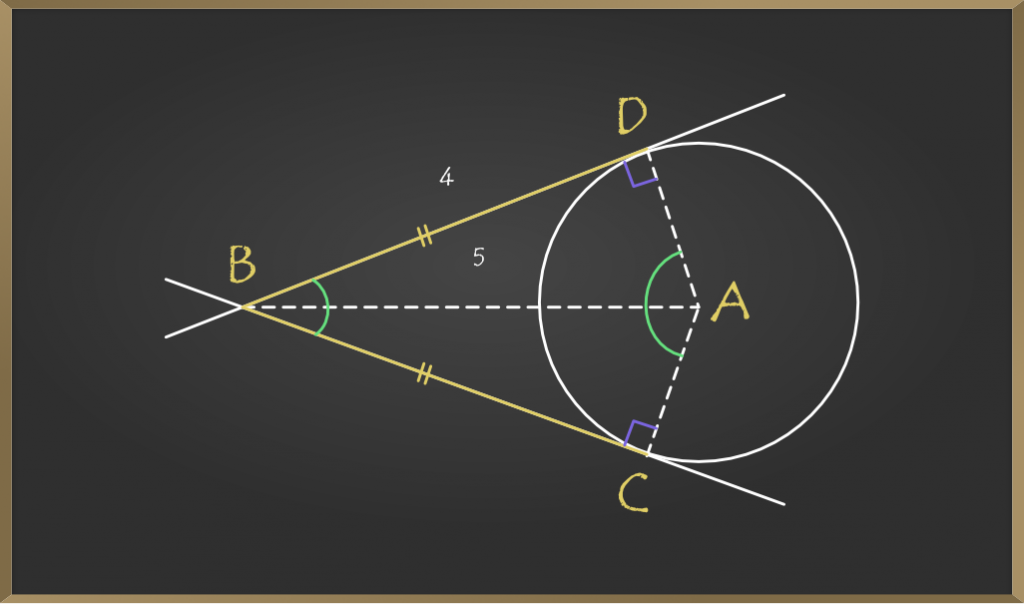
Theorem The Lengths Of Tangents Drawn From An External Point To A Tangents, secants, arcs and their angles. the theorems and formula for the rules for theses intersections. In trigonometry, the tangent function is used to find the slope of a line between the origin and a point representing the intersection between the hypotenuse and the altitude of a right triangle. however, in both trigonometry and geometry, tangent represents the slope of some object. In this article, we explored tangent in geometry. we learned that a tangent is a line that touches a circle at one point, known as the point of tangency. we also learned that a right angle forms between the tangent line and the radius of the circle, and that tangent can be used to measure circles. The simplest definition of the tangent uses the ratios of the sides of a right triangle, and modern methods express this function as the sum of an infinite series. tangents can be calculated directly when the lengths of the sides of the right triangle are known and can also be derived from other trigonometric functions.

Theorem 10 2 Class 10 Tangents From External Point Of Circle Are In this article, we explored tangent in geometry. we learned that a tangent is a line that touches a circle at one point, known as the point of tangency. we also learned that a right angle forms between the tangent line and the radius of the circle, and that tangent can be used to measure circles. The simplest definition of the tangent uses the ratios of the sides of a right triangle, and modern methods express this function as the sum of an infinite series. tangents can be calculated directly when the lengths of the sides of the right triangle are known and can also be derived from other trigonometric functions.

Theorem 10 2 Class 10 Tangents From External Point Of Circle Are