
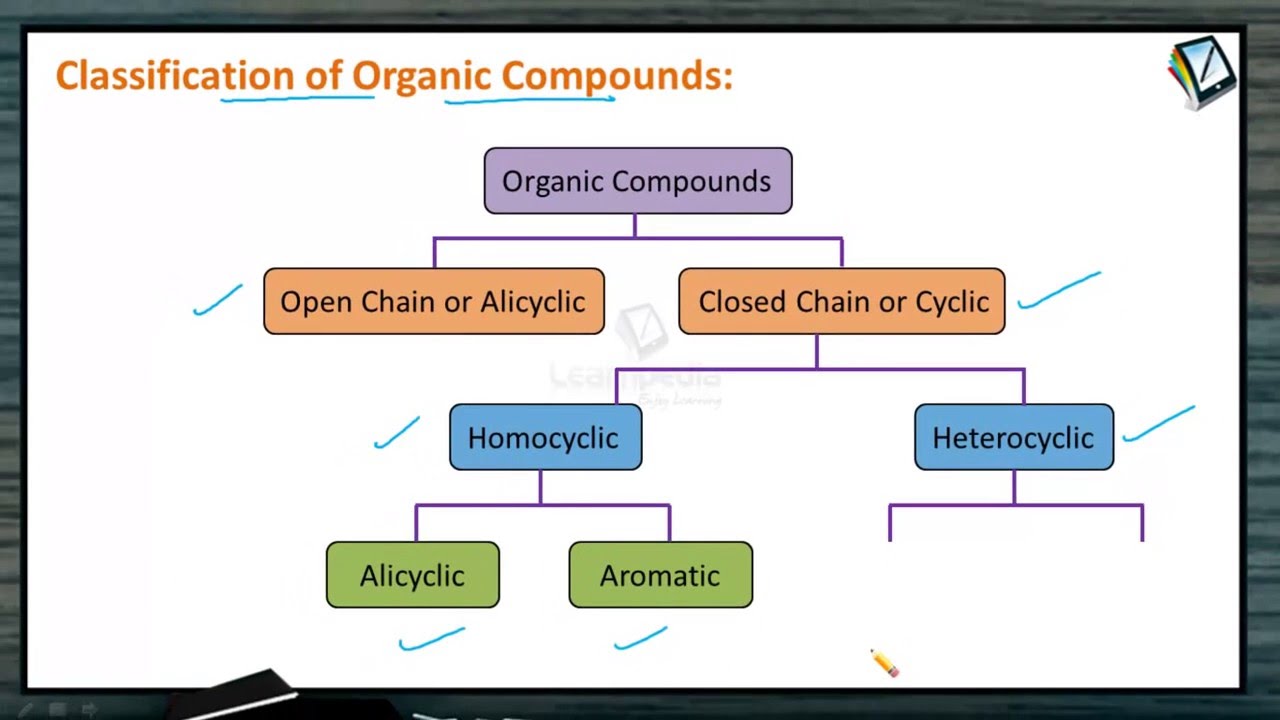
Classification And Identification Of Organic Molecules Based On Organic compounds are classified into several major categories based on the functional groups they contain. in the systematic names of organic compounds, numbers indicate the positions of functional groups in the basic hydrocarbon framework. Functional groups are structural units that determine the chemical reactivity of a molecule under a given set of conditions. organic compounds are classified into several major categories based on the functional groups they contain.

The Representative Functional Groups And Classes Of Organic Compounds Each of the four types of macromolecules—proteins, lipids, carbohydrates, and nucleic acids—has its own characteristic set of functional groups that contributes greatly to its differing chemical properties and its function in living organisms. In this tutorial, you will learn what exactly functional groups are and why they are important in organic chemistry. you will also learn how to easily identify the different classes of groups in organic compounds in order to assist with your problem solving. Functional groups are the property decider of a compound. a functional group is capable of controlling the nature of reaction chemistry. according to the behaviour of a functional group, the chemical synthesis track is chalked out for a specific type of reaction. Functional groups are specific groupings of atoms within molecules that have their own characteristic properties, regardless of the other atoms present in a molecule. common examples are alcohols, amines, carboxylic acids, ketones, and ethers.
Functional Groups Of Organic Compounds Functional groups are the property decider of a compound. a functional group is capable of controlling the nature of reaction chemistry. according to the behaviour of a functional group, the chemical synthesis track is chalked out for a specific type of reaction. Functional groups are specific groupings of atoms within molecules that have their own characteristic properties, regardless of the other atoms present in a molecule. common examples are alcohols, amines, carboxylic acids, ketones, and ethers. A functional group is a specific atom or group of atoms within a molecule that is responsible for its chemical properties and reactivity, while a homologous series is a family of organic compounds that share the same functional group and have similar chemical properties. Functional groups are specific arrangements of atoms within organic molecules that determine their chemical properties. The functional groups are the reactive group present in compounds that determine the chemical properties of these compounds. eg: oh, f, cho, cooh. this includes alkane, alkene, alkyne, and benzene derivatives. In this article, we have explored the top 10 functional groups that shape organic chemistry. from the common hydroxyl group in alcohols to the reactive halide groups, each functional group offers unique insights into molecular behavior and reactivity.