Visual Field Defects Visual Cortex Optic Neuritis Opt Vrogue Co Visual fields are useful in monitoring progression or recurrence of disease and guide treatment for conditions such as idiopathic intracranial hypertension (iih), optic neuropathy from multiple sclerosis, pituitary adenomas, and other sellar lesions. We evaluated the visual system at the retina optic nerve level and throughout the visual pathway, progressing from anterior to posterior structures, including the impact of secondary axon loss through retrograde degeneration due to lesions beyond the lateral geniculate nucleus.

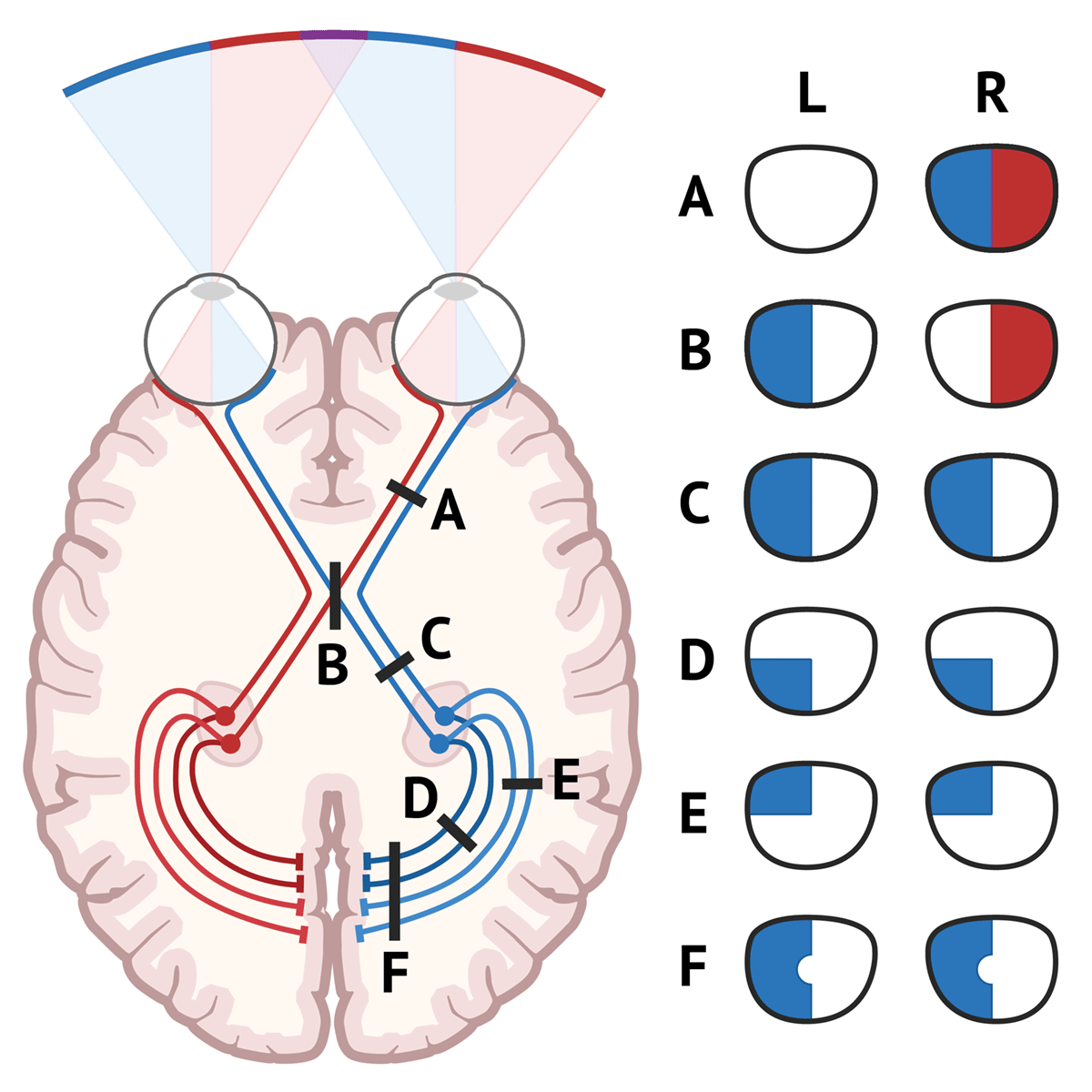
Visual Field Defects Visual Cortex Optic Neuritis Opt Vrogue Co The visual pathway comprises the retina, optic nerve, optic chiasm, optic radiations, and the visual centre in the occipital lobe. optic nerve lesions tend to cause ipsilateral monocular blindness. Visual field defects are a conglomerate of patterns of visual impairment derived from diseases affecting the optic nerve as it extends from the globe to the visual cortex. they are complex signs requiring perimetry or visual confrontation for delineation and are associated with diverse aetiologies. Before we dive into vf defects associated with optic nerve dz it can be challenging to distinguish between subtle retinal dz (specifically, a maculopathy) and optic nerve dz. let’s review some non vf clues that can help in this regard. for each finding, indicate whether optic neuropathy or maculopathy is more likely. if the pt has. The optic pathway includes the retina, optic nerve, optic chiasm, optic radiations, and occipital cortex (see figure higher visual pathways). damage along the optic pathway causes a variety of visual field defects.
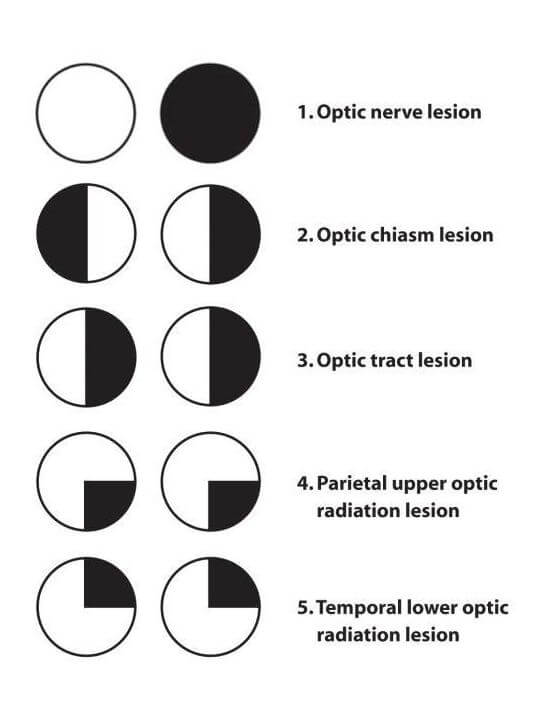
Visual Field Defects Visual Cortex Optic Neuritis Opt Vrogue Co Before we dive into vf defects associated with optic nerve dz it can be challenging to distinguish between subtle retinal dz (specifically, a maculopathy) and optic nerve dz. let’s review some non vf clues that can help in this regard. for each finding, indicate whether optic neuropathy or maculopathy is more likely. if the pt has. The optic pathway includes the retina, optic nerve, optic chiasm, optic radiations, and occipital cortex (see figure higher visual pathways). damage along the optic pathway causes a variety of visual field defects. Visual field defects are a conglomerate of patterns of visual impairment derived from diseases affecting the optic nerve as it extends from the globe to the visual cortex. they are complex signs requiring perimetry or visual confrontation for delineation and are associated with diverse aetiologies. The overall route is from the retina, through the optic nerve, to the optic chiasma (where the nasal retina (and the temporal visual field) crosses over to the opposite side, the temporal retina (nasal visual field) stays in place), then to the optic tract, then the lateral geniculate nucleus, then the primary visual cortex. Optic neuritis is a condition that involves primary inflammation of the optic nerve. it is usually. associated with an acute, often monocular vision loss with painful eye movement. optic neuritis. can be classified according to its appearance under ophthalmoscope or by its’ etiology. Conclusions: diffuse and central loss were more predominant in the affected eye at baseline, and nerve fiber bundle defects (partial arcuate, paracentral, and arcuate) were the most predominant localized abnormalities in both the affected and fellow eyes during the study.