Uniform Circular Motion Definition Laws Formula Examples Videos We travel to an amusement park to explore circular motion. we work through an example problem and define such terms as tangential velocity and centripetal acceleration. In physics, circular motion is movement of an object along the circumference of a circle or rotation along a circular arc. it can be uniform, with a constant rate of rotation and constant tangential speed, or non uniform with a changing rate of rotation.

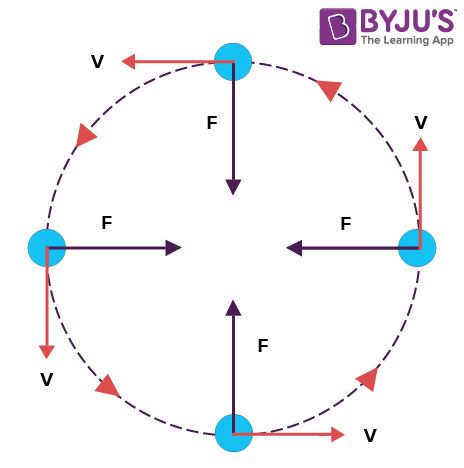
Circular Motion Physics Centripetal Force Velocity A particle is said to execute circular motion when it moves along the circumference of a circular path. an important aspect of circular motion is that the direction of motion is changing continuously unlike in the case of linear motion. The simplest case of circular motion is uniform circular motion, where an object travels a circular path at a constant speed. note that, unlike speed, the linear velocity of an object in circular motion is constantly changing because it is always changing direction. In physics, circular motion can be defined as the motion in which an object moves when it follows a circular path. in circular motion the object generally moves around a fixed point and the distance between the object and the fixed point is generally fixed. What is circular motion? circular motion is the movement of an object along the circumference of a circle or a circular path. this motion involves a continuous change in direction, leading to centripetal acceleration towards the center of the circle, essential in understanding rotational dynamics.

Circular Motion Unifyphysics In physics, circular motion can be defined as the motion in which an object moves when it follows a circular path. in circular motion the object generally moves around a fixed point and the distance between the object and the fixed point is generally fixed. What is circular motion? circular motion is the movement of an object along the circumference of a circle or a circular path. this motion involves a continuous change in direction, leading to centripetal acceleration towards the center of the circle, essential in understanding rotational dynamics. Explore the fundamentals of circular motion, including key concepts, formulas, and real world applications. dive into the physics of objects moving in circles, from planets in orbit to everyday mechanical devices. We will see that unlike linear motion, where velocity and acceleration are directed along the line of motion, in circular motion the direction of velocity is always tangent to the circle. this means that as the object moves in a circle, the direction of the velocity is always changing. Circular motion is a fundamental concept in physics, characterized by the movement of an object along a circular path. this type of motion is governed by two crucial elements: centripetal force and velocity. A circular motion refers to an object’s motion in a circular path. uniform circular motion occurs when the object moves at a constant linear speed. an object prescribing a circular path has a well defined velocity with magnitude and direction.